간략 정의
The Command Pattern encapsulates a request as an object, thereby letting you parameterize other objects with different requests, queue or log requests, and support undoable operations.
커맨드 패턴은 객체의 요청을 캡슐화한다. 이를 통해 다른 객체의 다른 요청을 매개변수화할 수 있으며 큐, 로그 요청 그리고 실행 취소 명령을 지원할 수 있다.Eric Freeman, Elisabeth Robson, “Head First Design Patterns, 2nd Edition”, O’Reilly Media, Inc., 2020
책에서는 전등, 문 개폐 등을 하나의 요청으로 사용할 수 있는 예제로 커맨드 패턴을 소개하고 있다. 필자도 비슷한 예제를 가져왔다. 커맨드 패턴의 컨셉은 전등을 키고 끄고, 문을 열고 닫고, 티비를 켜고 끄고 등을 on, off 라는 동작으로 볼 수 있다는 것이다. on 과 off 는 각각 execute 로 볼 수 있다. 즉 무엇을 실행하기 때문이다. 커맨드 패턴은 execute 하나로 액션을 실행하는 것이다. 이와 같이 execute 하나의 메서드로 관리할 때 장점은 캡슐화는 물론이고 확장성이 넓다. 일례로는 undo, redo, logging, queue 등이 있다.

Keyword
Client: Command 객체를 생성하는 책임을 가진다.
Receiver: Command 에서 execute 를 실행할 때 필요하다. Command 객체가 action 과 Receiver 를 감싸고 있다.
Invoker: Client 에서 Invoker 객체를 통해 setCommand 를 호출한다. 그리고 Command 객체에 전달하여 필요할 때까지 저장한다.
Command: 하나의 메소드만 제공하여 캡슐화를 제공한다. Receiver 통해 호출된다.
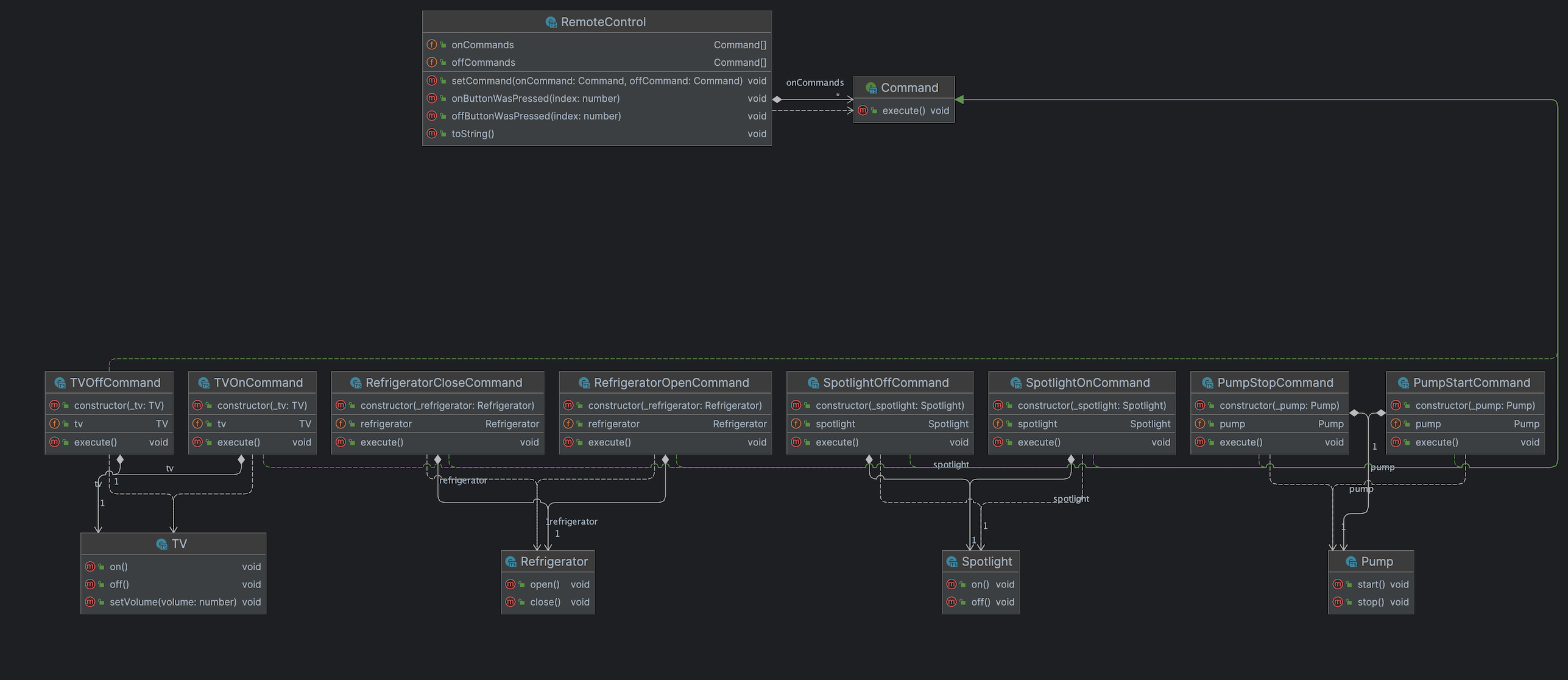
Class Diagram
기존
패턴 적용
Code
기존
class Pump {
start() {
console.log('Pump started');
}
stop() {
console.log('Pump stopped');
}
}
class Refrigerator {
open() {
console.log('Refrigerator opened');
}
close() {
console.log('Refrigerator closed');
}
}
class TV {
on() {
console.log('TV on');
}
off() {
console.log('TV off');
}
setVolume() {
console.log('Volume set');
}
}
class Spotlight {
on() {
console.log('Spotlight on');
}
off() {
console.log('Spotlight off');
}
}
new Pump().start(); // Pump started
new Pump().stop(); // Pump stopped
new Refrigerator().open(); // Refrigerator opened
new Refrigerator().close(); // Refrigerator closed
new TV().on(); // TV on
new TV().off(); // TV off
new TV().setVolume(); // Volume set
new Spotlight().on(); // Spotlight on
new Spotlight().off(); // Spotlight off
패턴 적용
Invoker: RemoteControl
Command: PumpStartCommand, PumpStopCommand, RefrigeratorOpenCommand, RefrigeratorCloseCommand, TVOnCommand, TVOffCommand, TVSetVolumeCommand, SpotlightOnCommand, SpotlightOffCommand
Receiver: Pump, Refrigerator, TV, Spotlight
interface Command {
execute(): void;
}
class PumpStartCommand implements Command {
pump: Pump;
constructor(_pump: Pump) {
this.pump = _pump;
}
execute() {
this.pump.start();
}
}
class PumpStopCommand implements Command {
pump: Pump;
constructor(_pump: Pump) {
this.pump = _pump;
}
execute() {
this.pump.stop();
}
}
class RefrigeratorOpenCommand implements Command {
refrigerator: Refrigerator;
constructor(_refrigerator: Refrigerator) {
this.refrigerator = _refrigerator;
}
execute() {
this.refrigerator.open();
}
}
class RefrigeratorCloseCommand implements Command {
refrigerator: Refrigerator;
constructor(_refrigerator: Refrigerator) {
this.refrigerator = _refrigerator;
}
execute() {
this.refrigerator.close();
}
}
class TVOnCommand implements Command {
tv: TV;
constructor(_tv: TV) {
this.tv = _tv;
}
execute() {
this.tv.on();
this.tv.setVolume(12);
}
}
class TVOffCommand implements Command {
tv: TV;
constructor(_tv: TV) {
this.tv = _tv;
}
execute() {
this.tv.off();
}
}
class SpotlightOnCommand implements Command {
spotlight: Spotlight;
constructor(_spotlight: Spotlight) {
this.spotlight = _spotlight;
}
execute() {
this.spotlight.on();
}
}
class SpotlightOffCommand implements Command {
spotlight: Spotlight;
constructor(_spotlight: Spotlight) {
this.spotlight = _spotlight;
}
execute() {
this.spotlight.off();
}
}
class Pump {
start() {
console.log('Pump started');
}
stop() {
console.log('Pump stopped');
}
}
class Refrigerator {
open() {
console.log('Refrigerator opened');
}
close() {
console.log('Refrigerator closed');
}
}
class TV {
on() {
console.log('TV on');
}
off() {
console.log('TV off');
}
setVolume(volume: number) {
console.log(`Volume set to ${volume}`);
}
}
class Spotlight {
on() {
console.log('Spotlight on');
}
off() {
console.log('Spotlight off');
}
}
class SimpleRemoteControl {
slot?: Command;
setCommand(command: Command) {
this.slot = command;
}
buttonWasPressed() {
this.slot?.execute();
}
}
class RemoteControl {
onCommands: Command[] = [];
offCommands: Command[] = [];
setCommand(onCommand: Command, offCommand: Command) {
this.onCommands.push(onCommand);
this.offCommands.push(offCommand);
}
onButtonWasPressed(index: number) {
this.onCommands[index].execute();
}
offButtonWasPressed(index: number) {
this.offCommands[index].execute();
}
toString() {
for (let i = 0; i < this.onCommands.length; i++) {
console.log(`[slot ${i}] ${this.onCommands[i].constructor.name} ${this.offCommands[i].constructor.name}`);
}
}
}
class RemoteLoader {
main() {
const remoteControl = new RemoteControl();
const spotlight = new Spotlight();
const pump = new Pump();
const refrigerator = new Refrigerator();
const tv = new TV();
const spotlightOn = new SpotlightOnCommand(spotlight);
const spotlightOff = new SpotlightOffCommand(spotlight);
const pumpStart = new PumpStartCommand(pump);
const pumpStop = new PumpStopCommand(pump);
const refrigeratorOpen = new RefrigeratorOpenCommand(refrigerator);
const refrigeratorClose = new RefrigeratorCloseCommand(refrigerator);
const tvOn = new TVOnCommand(tv);
const tvOff = new TVOffCommand(tv);
remoteControl.setCommand(spotlightOn, spotlightOff); // [slot 0] SpotlightOnCommand SpotlightOffCommand
remoteControl.setCommand(pumpStart, pumpStop); // [slot 1] PumpStartCommand PumpStopCommand
remoteControl.setCommand(refrigeratorOpen, refrigeratorClose); // [slot 2] RefrigeratorOpenCommand RefrigeratorCloseCommand
remoteControl.setCommand(tvOn, tvOff); // [slot 3] TVOnCommand TVOffCommand
remoteControl.toString();
remoteControl.onButtonWasPressed(0); // Spotlight on
remoteControl.offButtonWasPressed(0); // Spotlight off
remoteControl.onButtonWasPressed(1); // Pump started
remoteControl.offButtonWasPressed(1); // Pump stopped
remoteControl.onButtonWasPressed(2); // Refrigerator opened
remoteControl.offButtonWasPressed(2); // Refrigerator closed
remoteControl.onButtonWasPressed(3); // TV on
remoteControl.offButtonWasPressed(3); // Volume set to 12
}
}
new RemoteLoader().main();
실제 사용 느낌
특정 상태를 저장하고 실행할 때 매우 유용할 것 같다. 이유는 실행과 실행 취소(undo) 를 지원하는데 우아하게 만들 수 있기 때문이다.
실상은 각기 다른 일들을 하지만 execute 라는 메서드로 감싸 실행하도록하여 재사용성을 높일 수 있다는 장점이 있다. 또한 조합하기도 쉽다. 공통적으로 처리한다는 것은 결합도를 낮출 수 있지만 과도하게 사용할 시 오히려 클래스들이 난잡하게 펼쳐질 것 같다.
