수레 움직이기
문제 설명
n x m 크기 격자 모양의 퍼즐판이 주어집니다.
퍼즐판에는 빨간색 수레와 파란색 수레가 하나씩 존재합니다. 각 수레들은 자신의 시작 칸에서부터 자신의 도착 칸까지 이동해야 합니다.
모든 수레들을 각자의 도착 칸으로 이동시키면 퍼즐을 풀 수 있습니다.
당신은 각 턴마다 반드시 모든 수레를 상하좌우로 인접한 칸 중 한 칸으로 움직여야 합니다. 단, 수레를 움직일 때는 아래와 같은 규칙이 있습니다.
수레는 벽이나 격자 판 밖으로 움직일 수 없습니다.
수레는 자신이 방문했던 칸으로 움직일 수 없습니다.
자신의 도착 칸에 위치한 수레는 움직이지 않습니다. 계속 해당 칸에 고정해 놓아야 합니다.
동시에 두 수레를 같은 칸으로 움직일 수 없습니다.
수레끼리 자리를 바꾸며 움직일 수 없습니다.
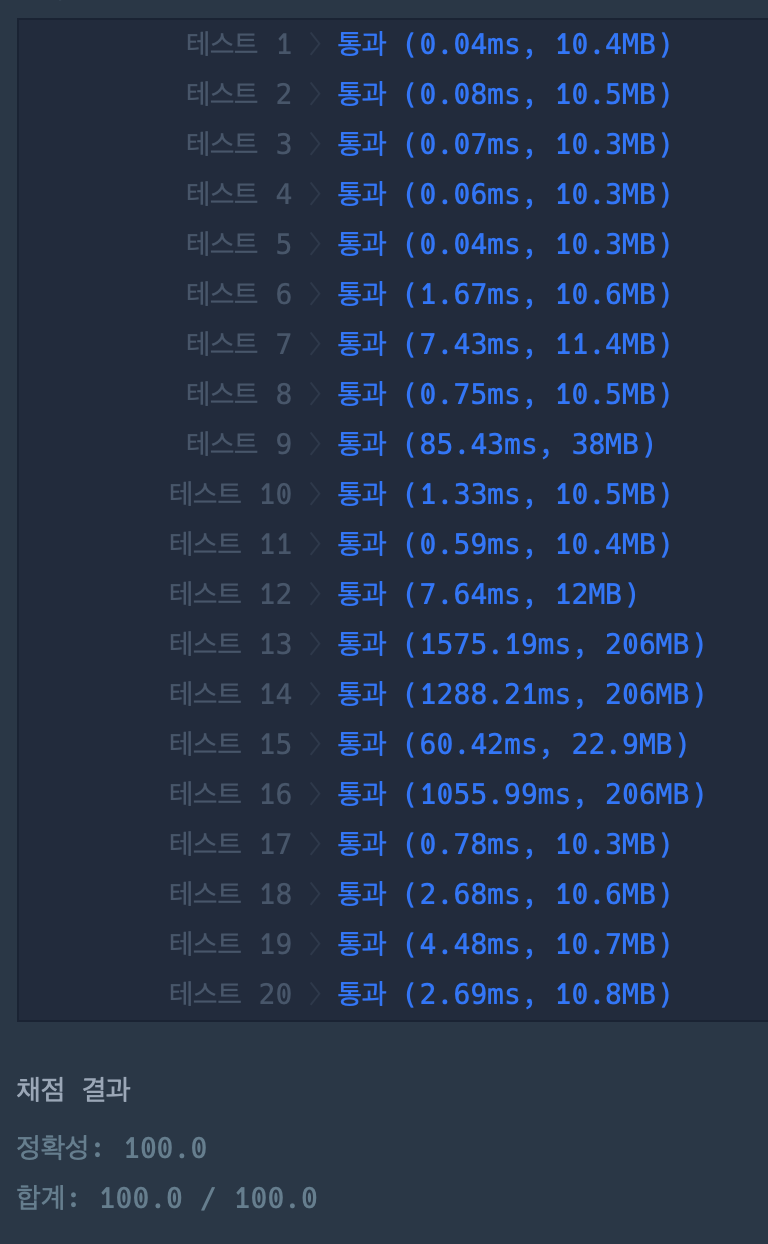
시각화
아래와 같이 정보가 주어졌다.
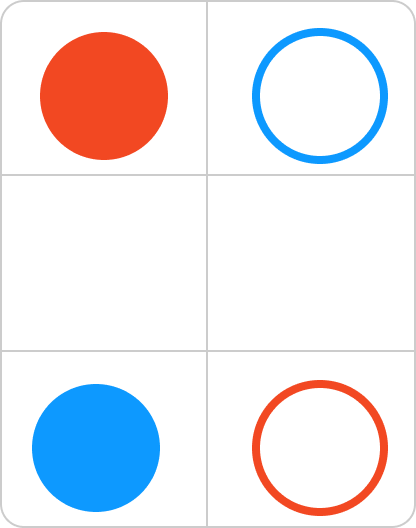
3턴이 지나면 각자 도착지점에 도착하게 된다.
문제 해결 과정
제한사항을 보면 가로, 세로가 최대 4이다. 그렇기에 BFS 로 풀어되겠다고 생각했다. 어떻게 보면 제한사항이 많고 1턴마다 2개가 움직여야하는 것을 제외하고는 특별한 것은 없다.
문제 설명에 나온 것처럼 제한 사항은 아래와 같다.
- 각 수레는 같은 칸에 위치할 수 없다.
- 수레는 벽이나 격자 판 밖으로 움직일 수 없다.
- 수레는 자신이 방문했던 칸으로 움직일 수 없다.
- 자신의 도착 칸에 위치한 수레는 움직이지 않는다.
- 수레끼리 자리를 바꾸며 움직일 수 없다.
기본적인 로직을 작성하면서 위 조건을 만족하도록 코드를 작성해보자.
각 수레 좌표와 목표 좌표 찾기
1 ~ 5 값이 있는데 5는 벽이고 1, 2, 3, 4는 각각 빨간 수레, 파란 수레, 빨간 수레 목표, 파란 수레 목표이다.
for y, row in enumerate(maze):
for x, col in enumerate(row):
if col == 1:
red_yx = (y, x)
if col == 2:
blue_yx = (y, x)
if col == 3:
target_red_yx = (y, x)
if col == 4:
target_blue_yx = (y, x)
각 수레 움직임 경우의 수 구하기
product 는 데카르트 곱을 구하는 함수이다. 파이썬인 경우 간편하게 import 해서 사용하면 되지만 다른 언어의 경우 데카르트 곱을 구하는 함수를 만들어서 사용하면 된다.
move_pos = list(product([(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)], repeat=2))
수레는 상하좌우로 움직일 수 있으므로 위와 같이 4가지 경우의 수를 구했다. 수레가 2개이기에 경우의 수도 4가지의 제곱이다.
즉 빨간 수레가 상하좌우로 움직일 수 있는 경우의 수는 4가지이고, 파란 수레가 상하좌우로 움직일 수 있는 경우의 수도 4가지이다. 그렇기에 두 수레가 움직일 수 있는 경우의 수는 4가지의 제곱이다.
BFS 로직 구현
아래 코드는 BFS 안에 들어갈 허용하지 않는 케이스이다.
좌표를 벗어난 경우
if (red_yx[0] < 0 or red_yx[0] >= len(maze)) or (red_yx[1] < 0 or red_yx[1] >= len(maze[0])):
continue
if (blue_yx[0] < 0 or blue_yx[0] >= len(maze)) or (blue_yx[1] < 0 or blue_yx[1] >= len(maze[0])):
continue
왔던 곳인 경우
if (red_yx != target_red_yx and ''.join(map(str, list(red_yx))) in red_history) or (
blue_yx != target_blue_yx and ''.join(map(str, list(blue_yx))) in blue_history):
continue
벽에 부딪힌 경우
if maze[red_yx[0]][red_yx[1]] == 5 or maze[blue_yx[0]][blue_yx[1]] == 5:
continue
두 수레가 같은 위치에 있는 경우
if red_yx == blue_yx:
continue
두 수레가 서로 위치를 바꾸는 경우
if next_red_yx == blue_yx and next_blue_yx == red_yx:
continue
이미 한 수레가 목표에 도달한 경우
한 수레가 이미 목표에 도착한 경우 움직이지 않아야한다.
next_red_yx = red_yx if red_yx == target_red_yx else (red_yx[0] + v[0][0], red_yx[1] + v[0][1])
next_blue_yx = blue_yx if blue_yx == target_blue_yx else (blue_yx[0] + v[1][0], blue_yx[1] + v[1][1])
위 논리를 조합해서 BFS 를 구현하는 아래 전체 코드와 같다.
전체 코드
위 논리를 코드로 적으면 아래와 같다.
from collections import deque
from itertools import product
def solution(maze):
def bfs():
min_dist = float('inf')
red_yx, blue_yx, target_red_yx, target_blue_yx = (0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0), (0, 0)
move_pos = list(product([(-1, 0), (1, 0), (0, 1), (0, -1)], repeat=2))
for y, row in enumerate(maze):
for x, col in enumerate(row):
if col == 1:
red_yx = (y, x)
if col == 2:
blue_yx = (y, x)
if col == 3:
target_red_yx = (y, x)
if col == 4:
target_blue_yx = (y, x)
q = deque([((red_yx[0], red_yx[1]), (blue_yx[0], blue_yx[1]), {}, {})])
while q:
red_yx, blue_yx, red_history, blue_history = q.popleft()
if min_dist <= len(red_history):
continue
if red_yx == target_red_yx and blue_yx == target_blue_yx:
if max(len(red_history), len(blue_history)) < min_dist:
min_dist = max(len(red_history), len(blue_history))
continue
if (red_yx[0] < 0 or red_yx[0] >= len(maze)) or (red_yx[1] < 0 or red_yx[1] >= len(maze[0])):
continue
if (blue_yx[0] < 0 or blue_yx[0] >= len(maze)) or (blue_yx[1] < 0 or blue_yx[1] >= len(maze[0])):
continue
if maze[red_yx[0]][red_yx[1]] == 5 or maze[blue_yx[0]][blue_yx[1]] == 5:
continue
if (red_yx != target_red_yx and ''.join(map(str, list(red_yx))) in red_history) or (
blue_yx != target_blue_yx and ''.join(map(str, list(blue_yx))) in blue_history):
continue
if red_yx == blue_yx:
continue
red_history[''.join(map(str, list(red_yx)))] = True
blue_history[''.join(map(str, list(blue_yx)))] = True
for v in move_pos:
next_red_yx = red_yx if red_yx == target_red_yx else (red_yx[0] + v[0][0], red_yx[1] + v[0][1])
next_blue_yx = blue_yx if blue_yx == target_blue_yx else (blue_yx[0] + v[1][0], blue_yx[1] + v[1][1])
if next_red_yx == blue_yx and next_blue_yx == red_yx:
continue
q.append((next_red_yx, next_blue_yx, dict(red_history), dict(blue_history)))
return min_dist
answer = bfs()
return 0 if answer == float('inf') else answer